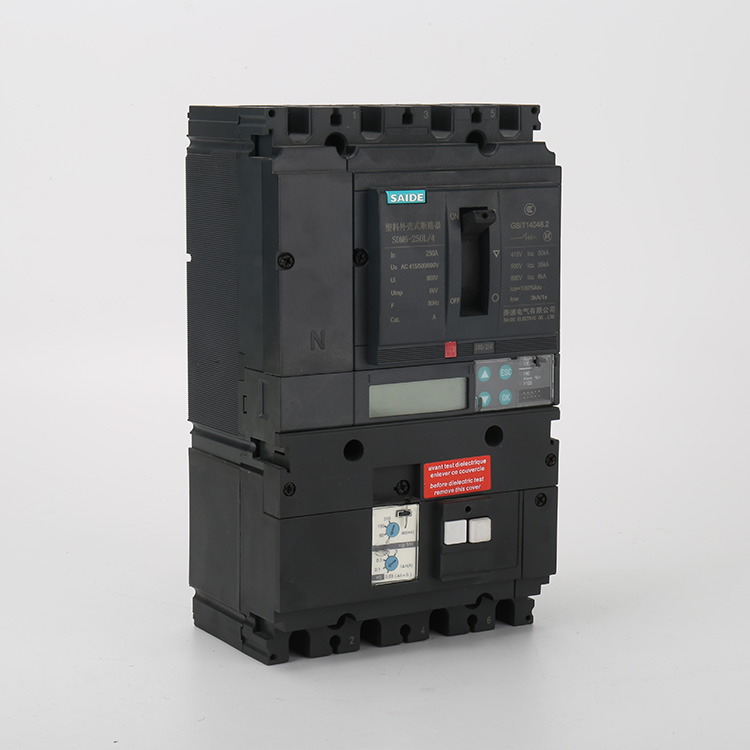
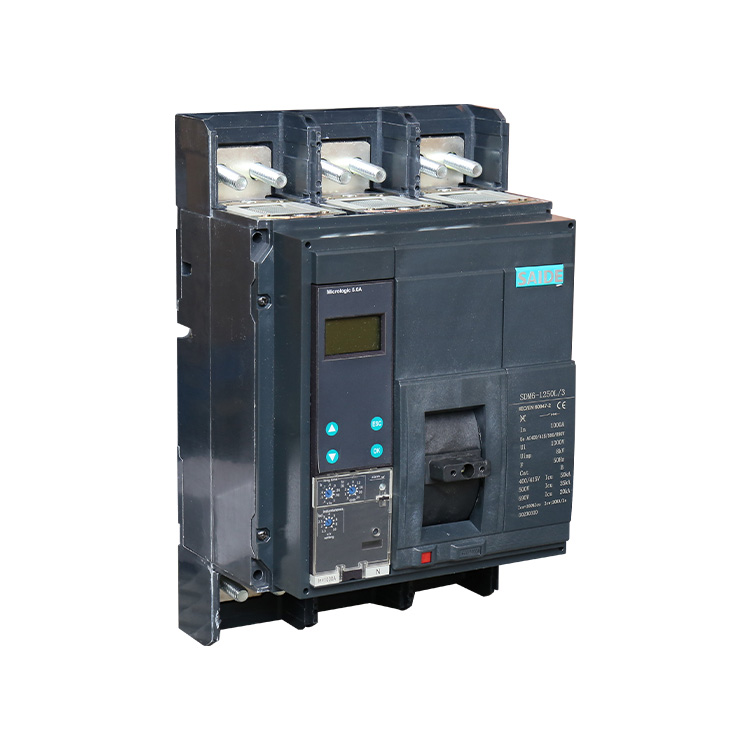
2000A Air Circuit Breaker
ACB stands for Air Circuit Breaker. Just like the MCCB breaker, the ACB derives its name from the fact that it uses air for insulation. In terms of construction, the 2000A Air Circuit Breaker(ACB) is made from a steel metal frame and the tripping mechanisms housed inside it.
Send Inquiry
ACBs are mainly built for use in high current applications such as power transmission lines and heavy industrial systems. In these cases, the ACB offers both overload and fault protection of the circuit – the same way that the MCCB protection does.
The 2000A Air Circuit Breaker refers to an electrical switching device that is designed to protect electrical circuits from excessive current.ACBs are commonly used in medium to high voltage applications, typically in industrial and commercial settings. They are designed to interrupt or disconnect the power supply when an abnormal current flow or fault condition occurs in the circuit. This helps to prevent damage to the electrical equipment, minimize the risk of fire or electrical hazards, and ensure the safety of personnel.
The ACB vs. MCCB comparison will include these differences:
ratings, size, and operating, voltage, and cost.The MCCB ratings for current usually range from a few amperes up to 800A, while ACB ratings for can go up to 6,300A.ACB has a much larger current-carrying capacity than an MCCB。 In addition, the user can also add more accessories to an ACB than an MCCB. These include auxiliary contacts and other release accessories. MCCB and ACB difference lies in the type of voltage they are rated for。The function of MCCB and ACB is to protect electrical systems and electrical equipment from damage by faults. However, because the breakers come with different voltage/current ratings, they are also used in different kinds of applications.n terms of price, an MCCB breaker is usually cheaper than an ACB. That’s because MCCBs have a lower current-carrying capacity and smaller size.